Applied Design Patterns with Java
Structural :: Composite (163) {C ch 11}
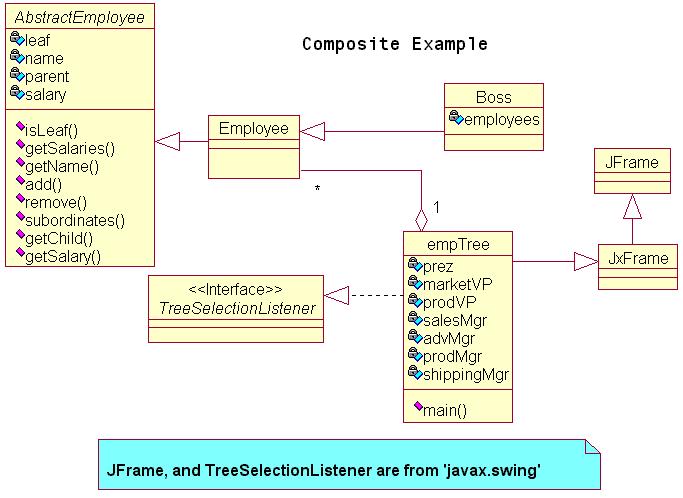
Example - UML : Employees
Example - Java :: Patterns\Structural\Composite
Pattern Concept: to create hierarchical, recursive objects so that any one of them may be either a Composite
or simple object; some objects may be nodes with branches, while others may be leaves.
Issues and Consequences of the Composite pattern include:
- Composite allows simple objects and complex objects to appear to be the same to the client;
- Composite allows easy adding of additional kinds of components, at the risk of over-generality (becoming
all things to all clients);
- It is very difficult to restrict what clients can do with components.
- The ordering or ranking of components may be needed.
If so, this functionality must be added;
- If the child objects have high update rates, parent caching
may be used to optimize. This adds more work and complexity to the solution.
The example Java program is called 'empTree'.
The UML diagram is above, and the list of Java files is
below:

Catalog Structural Prev Next


